Introduction
Food allergies are a growing concern among infants, yet they are often overlooked due to a lack of understanding. Food allergies can cause a wide range of stressors, both physical and emotional, and they are often difficult to identify. Identifying food allergies in infants is of great importance and can help prevent more serious reactions. This article will discuss the importance of identifying food allergies in infants, the signs and symptoms of food allergies, and what parents should do if they suspect their infant has a food allergy, so that they can steer away from unsafe foods.
What Parents Should Do
If you suspect that your infant has a food allergy, it is important to consult a doctor right away. Your doctor may order a food allergy test to confirm the diagnosis. The test can involve introducing a small dose of the suspected food to your infant and then monitoring them for an allergic reaction. If the test shows that your infant has an allergy, your doctor will provide you with a plan of action and a list of foods to avoid.
Signs and Symptoms: Recognizing the Most Common Indicators of a Food Allergy in Babies
When it comes to babies, recognizing signs and symptoms of a food allergy can be difficult for parents and caregivers. The most common indicators of food allergies in babies are:
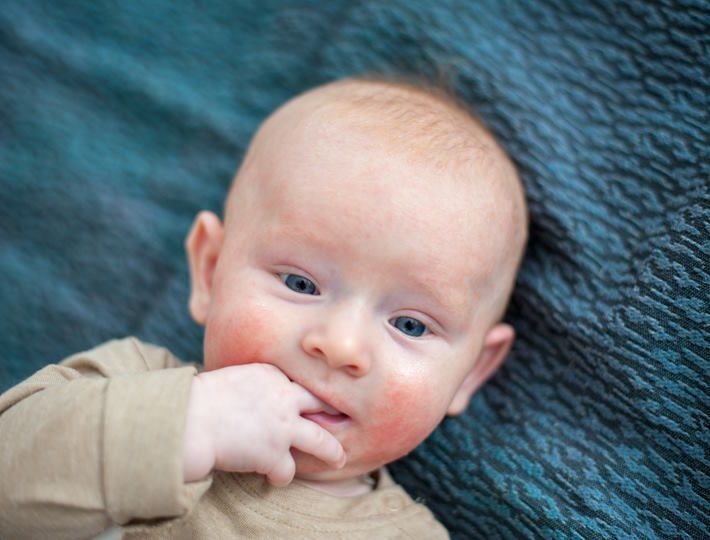
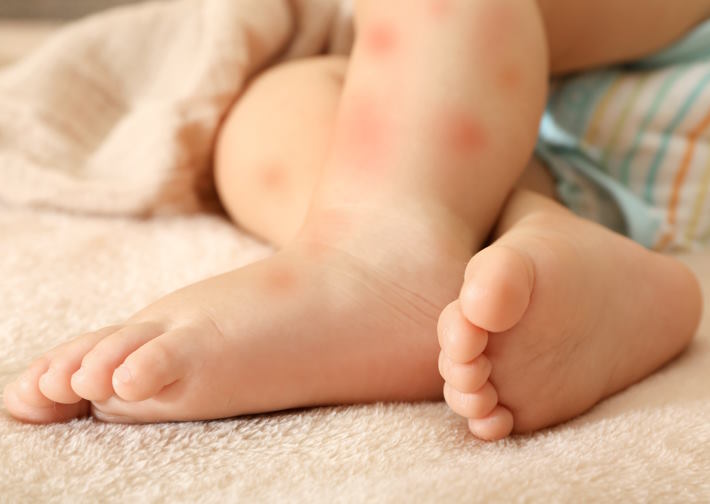
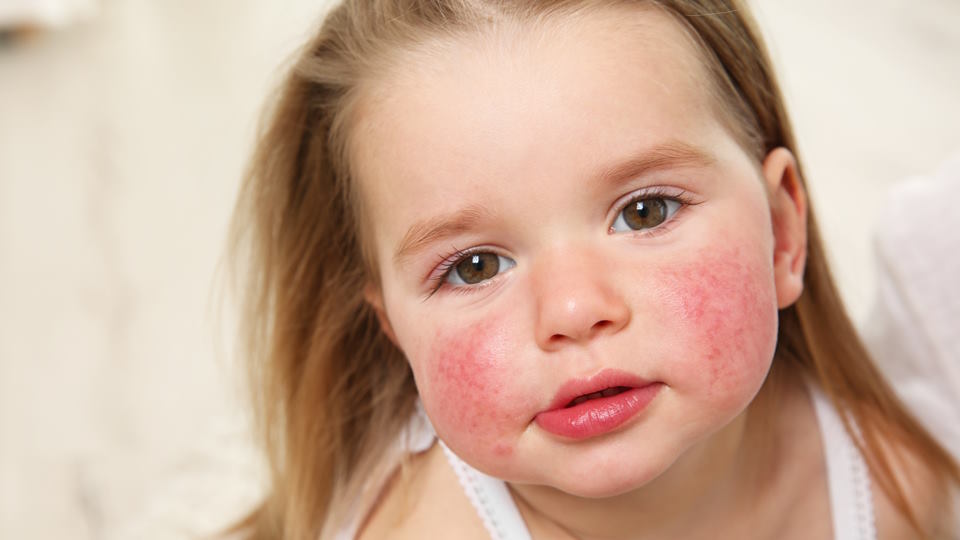
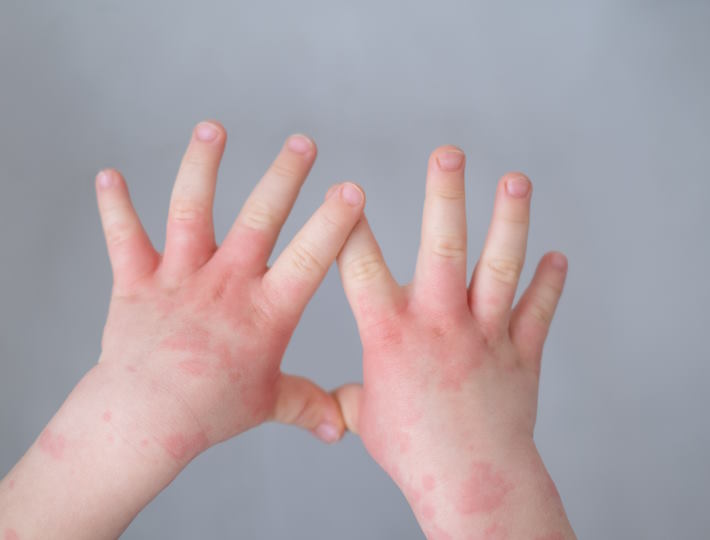
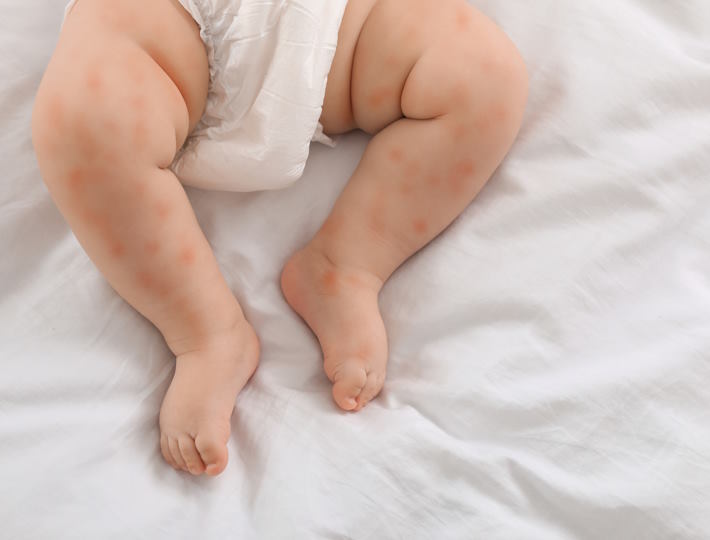
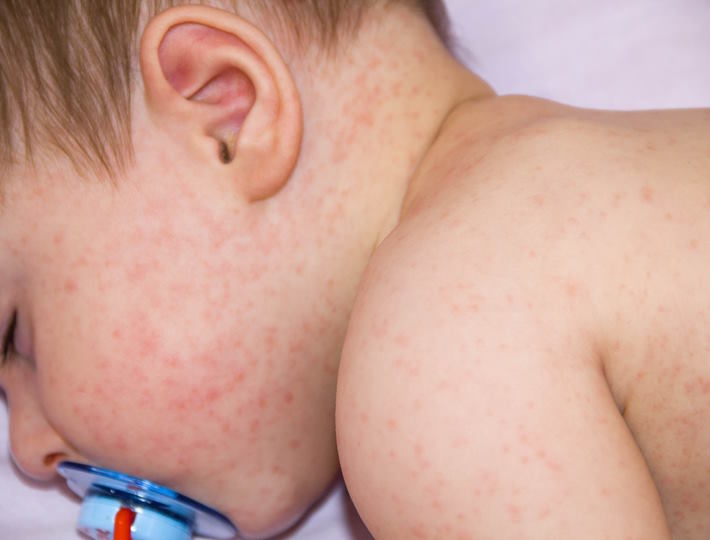
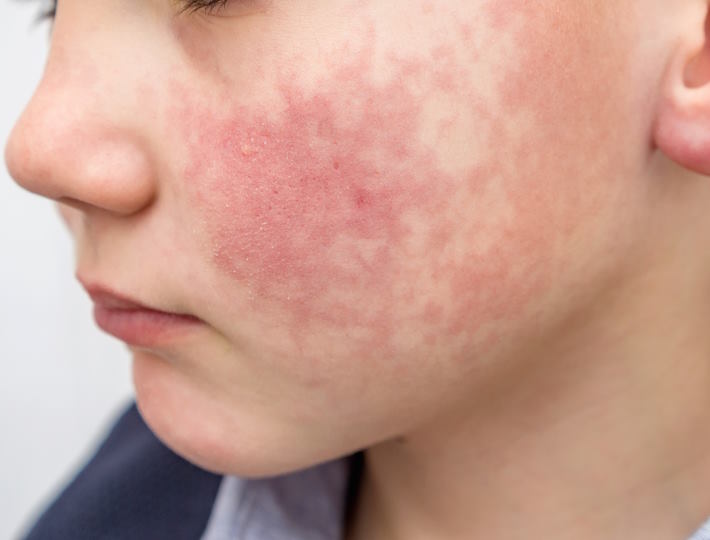
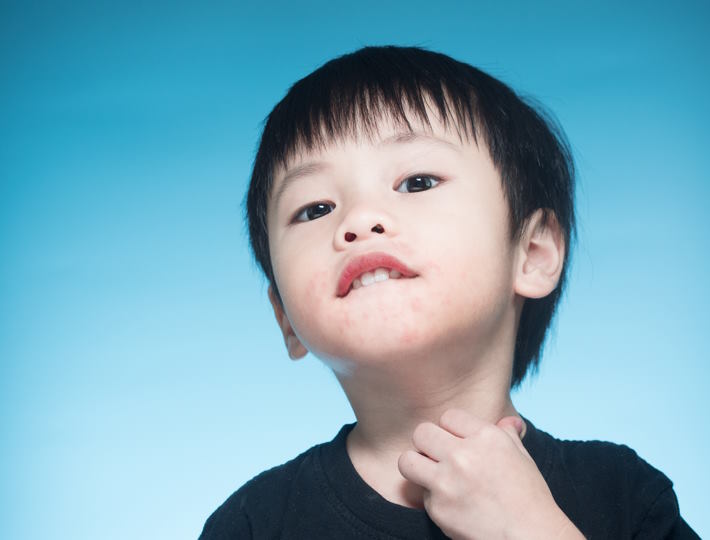
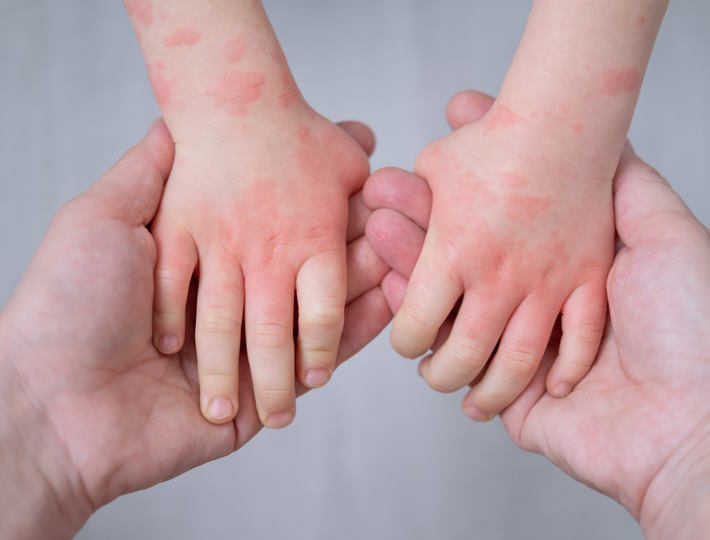
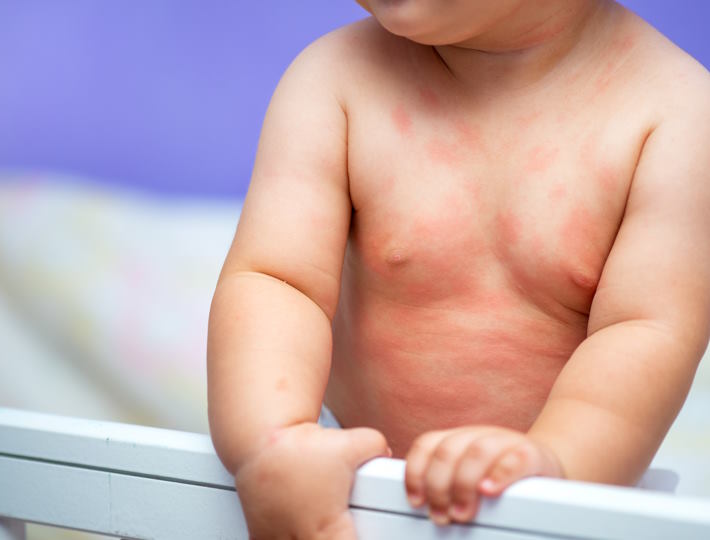
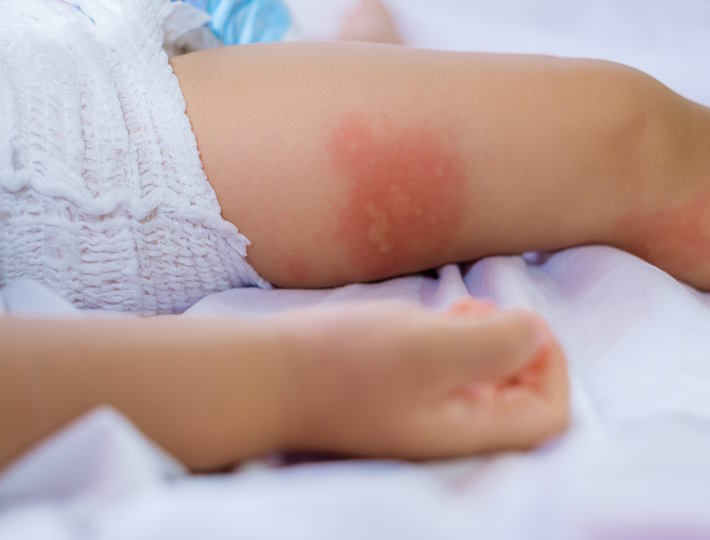
- Skin reactions, like hives, eczema, or redness
- Digestive issues, such as vomiting, diarrhea, or constipation
- Respiratory symptoms, including coughing, wheezing, or difficulty breathing
- Swelling, particularly of the face, tongue, or lips
If your baby is displaying any of these symptoms, it is important to speak with your doctor or a healthcare professional. They can help you determine if your baby has a food allergy and provide you with the best plan of action to manage it.
Reactions and Timing: Understanding Immediate Reactions and their Timing
Understanding how and why people react in a certain way to circumstances or events can help us better understand their behaviors and actions. When examining immediate reactions and their timing, it is important to consider a few key factors.
- It helps to have a clear understanding of the context in which the reaction occurs. What happened prior to the event? What is the perceived environment or climate? How are observers of the event interpreting the situation? This context can often provide clues to understanding the reaction.
- It is important to keep in mind the individual’s background and experience. How has this person reacted to similar circumstances in the past? What has been their experience in similar situations? These elements can help explain why the person might be responding in a certain way.
- It is important to consider the individual’s personality and traits. Are they generally known to be a calm, even-tempered person? Do they tend to be highly emotional in their reactions? These elements can provide helpful information when analyzing the reaction and its timing.
- It is important to consider the immediacy of the reaction. How long did it take for the reaction to occur? Was it instantaneous or delayed? How quickly did it occur in relation to the event? These elements can provide helpful insight into the intensity of the reaction and its meaning.
Finally, it is important to consider the long-term impact of the reaction. Was it a one-time occurrence or did it lead to further actions? Was it the beginning of a larger pattern? Understanding the long-term implications can help us better interpret the reaction and its timing.
Skin Symptoms: Exploring the Link between Skin Sensitivity and Food Allergies in Babies
Skin sensitivity and food allergies in babies can have a strong link. It is essential for parents to be aware of the signs and symptoms in order to provide the best care for their child. In some cases, skin sensitivity may be linked to an underlying food allergy. While not all skin sensitivities are related to food allergies, it is important to be aware of the connection between the two.
Signs & Symptoms of Skin Sensitivity
The signs and symptoms of skin sensitivities may include redness, inflammation, itching, flaking, dryness, and bumps. A baby may also experience hives, which are a reaction to the allergen and can appear on the face, arms, and legs. In more extreme cases, a baby may have an anaphylactic reaction, which can include difficulty breathing, dizziness, confusion, and shock.
Causes of Skin Sensitivity & Food Allergies
In some cases, skin sensitivity may be caused by an underlying food allergy. If this is the case, it is essential to identify the food that is causing the reaction and to avoid it going forward. Common food allergens in babies include dairy, eggs, soy, wheat, fish, shellfish, and peanuts. Food allergies can cause mild to severe reactions, so it is important to work with a doctor to determine the best course of treatment.
Diagnosis & Treatment
To diagnose skin sensitivity, a doctor may perform an allergy skin test or a blood test. In some cases, an elimination diet can also be used to isolate the allergen. Treatment may include the use of an anti-inflammatory cream or antihistamine, both of which can help to reduce the signs and symptoms of skin sensitivity. If the skin sensitivity is found to be caused by a food allergy, it may be necessary to avoid the allergen entirely.
Gastrointestinal Symptoms: Examining the Connection between Digestive Distress and Food Allergies in Babies
Babies are prone to a wide range of gastrointestinal issues, and for some, food allergies may be to blame. While it can be difficult to tell the difference between a food allergy and the common symptoms of gas, reflux, or constipation, understanding the connection between digestive distress and food allergies can help parents provide the best care for their little ones.
For some babies, food allergies can cause a variety of digestive symptoms including:
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Gas and bloating
- Excessive crying
When diagnosing a food allergy in babies, doctors will often begin by asking parents questions about their baby’s diet, feeding habits, and any signs of gastrointestinal distress. If the doctor believes a food allergy may be present, they may recommend a skin prick test, a blood test, or an elimination diet.
An elimination diet involves a temporary removal of all the potential food allergens from the baby’s diet. The list of eliminated foods will vary depending on the baby’s age and symptoms, but common allergens include cow’s milk, eggs, wheat, soy, peanuts, tree nuts, fish, and shellfish.
Once the potential allergen foods have been eliminated, the doctor may recommend adding back the foods one by one to observe the baby’s reaction. If the baby experiences a reaction within a few days of eating a food, that food may be the source of the allergy.
It is important to note that even if tests come back negative for food allergies, the baby may still experience digestive discomfort from foods that are hard to break down. Common offenders are cow’s milk and certain fruits and vegetables. Working with a pediatric dietician or nutritionist can help parents develop a feeding plan that is best suited for their baby’s needs.
Respiratory Symptoms: Assessing the Relationship between Respiratory Responses and Food Allergies in Babies
The relationship between respiratory symptoms and food allergies in babies is an important one to understand. Allergies can cause a range of respiratory complications in infants, making it important for parents and medical professionals to be aware of any potential triggers. The primary way to assess the relationship between respiratory responses and food allergies in babies is to recognize any signs of an allergic reaction, such as coughing, wheezing, nasal congestion, or difficulty breathing. Other signs may also be present, such as hives, eczema, or swelling of the lips and tongue.
It is also necessary to consider the particular food item that the baby has eaten and to perform tests to confirm an allergic reaction. To do this, the medical professional will likely conduct an allergen skin prick test or allergen-specific immunoglobulin E test. Once the exact allergen has been identified and a diagnosis of food allergy has been made, the reaction will be monitored and any specific treatments or medication prescribed.
In some cases, additional tests may be necessary to gain a better understanding of the baby’s individual allergic response, such as an oral food challenge. This will involve the baby eating a small amount of the allergen and being monitored for any signs or symptoms of an allergic reaction, both immediate and delayed. This is a valuable assessment tool in the diagnosis of food allergies in babies.
Anaphylaxis: Recognizing Severe Reactions and their Significance
Anaphylaxis is a severe and life-threatening allergic reaction that needs to be recognized and treated quickly. It typically occurs within minutes to hours of exposure to an allergen, and can affect several organs, including the skin, gastrointestinal system and respiratory system. Symptoms can range from mild to severe, and can include:
- Hives or itchy skin
- Swelling of the lips, tongue or throat
- Wheezing, coughing, or difficulty breathing
- Nausea, vomiting and/or abdominal pain
- Dizziness, confusion, or lightheadedness
If anaphylaxis is suspected, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. Treatment typically involves the administration of epinephrine as well as supportive care. Anaphylaxis can be fatal if not treated promptly, so it is important to be aware of the signs and symptoms that may indicate a severe reaction.
The importance of recognizing and treating anaphylaxis cannot be overstated. By increasing awareness and preparedness, we can help ensure that those at risk are better equipped to manage anaphylactic reactions, and that the medical community is better able to prevent and treat anaphylaxis more effectively.
Diagnosis: Differentiating Between Food Allergies, Intolerances, and Sensitivities in Babies
When it comes to food allergies, intolerances, and sensitivities in babies, diagnosis is key to understanding and navigating the foods that your baby can safely eat. Poor diagnosis or misdiagnosis can lead to an incorrect treatment plan, leading to more issues such as unnecessary eliminations of foods, gastrointestinal problems, and other issues that can affect a baby’s health and quality of life.
Here is a breakdown of how food allergies, intolerances, and sensitivities in babies can be diagnosed:
Food Allergy Diagnosis
When it comes to diagnosing food allergies in babies, the goal is to identify the specific food allergen that is causing the reaction. Depending on the symptoms, there are a few different tests that can be used to diagnose a food allergy in babies, including skin prick tests, blood tests, and elimination diets.
- Skin Prick Tests – During this test, a small amount of the suspected allergen is placed on the baby’s skin and a tiny prick is made. The skin will be monitored for any reactions, such as redness, swelling, or itching.
- Blood Tests – Blood tests can also be used to measure the presence of antibodies for specific allergens. The results of a blood test can help doctors determine which food allergens the baby is reacting to.
- Elimination Diets – Elimination diets involve removing potential allergens from the baby’s diet and then slowly reintroducing them to determine which foods are causing the reaction.
Food Intolerance and Sensitivity Diagnosis
When it comes to diagnosing food intolerances and sensitivities in babies, the goal is to identify which foods in the baby’s diet are causing the reaction. This can be done through a variety of tests, including food sensitivity tests, elimination diets, and careful observation.
- Food Sensitivity Tests – Food sensitivity tests look for specific foods that cause an immune system reaction in the baby’s body. These tests can measure the presence of antibodies for specific foods and can help to determine which foods the baby is reacting to.
- Elimination Diets – Elimination diets involve removing potential allergens from the baby’s diet and then slowly reintroducing them to determine which foods are causing the reaction.
- Observation – Careful observation of the baby’s reactions to different foods can help to identify which foods may be causing the reaction. It is important to pay attention to the timing, duration, and severity of the reactions in order to best diagnose which foods are causing the reaction.
Family History: The Influence of Family History and Prenatal Exposure to Allergens
Family history is an important factor in determining whether a person will develop allergies. Those with a family history of allergies are more likely to have allergies themselves. Research suggests that genetics can account for up to one-third of allergic disease. Family history is also important for prenatal exposure to allergens. It is suggested that a mother’s exposure to allergens before and during pregnancy can be passed onto the fetus, which may then cause the baby to have allergies or be more likely to develop allergies later in life.
This is why it is important for pregnant women to be screened for allergies and to avoid contact with allergens if possible. Additionally, it is important to note that genetics do not guarantee the development of allergies; an individual’s environment also plays an important role in determining whether they will develop allergies.
Diagnosis and Treatment: The Role of Doctors and Pediatricians in Diagnosing and Treating Food Allergies
Doctors and pediatricians are often the first point of contact for individuals or parents of children that are experiencing symptoms associated with a food allergy. Working with a medical professional is necessary to ensure a proper diagnosis, which requires the collection of medical history, physical examination, and allergy testing.
Allergy testing includes skin-prick testing, blood testing, and food challenge tests. A skin-prick test involves placing a small amount of a potential allergen on the skin and then pricking the skin so the allergen can come into contact with the immune system. Blood testing checks for certain IgE antibodies in the blood. A food challenge test is the only definitive test for a food allergy, and it involves consuming the food in question in a medical setting under the supervision of a healthcare professional.
Once a diagnosis of a food allergy has been confirmed, it’s important to work closely with the doctor or pediatrician to develop a comprehensive management plan. This plan may include:
- Avoidance of the specific food allergen and closely related foods
- Education about food labeling and food preparation
- Prescription and/or over-the-counter medications to treat reactions, such as antihistamines and epinephrine
- Regular follow-up appointments with the doctor or pediatrician
It’s also important to always carry an epinephrine auto-injector in case of a severe allergic reaction, as it can be life-saving.
A doctor or pediatrician plays an essential role in diagnosing and treating food allergies, so it’s critical to find a healthcare professional that is experienced in the diagnosis and management of food allergies.
Food Allergy Testing: Understanding the Process and Purpose of Testing for Food Allergies in Babies
Food allergies in babies can be serious health concerns, and proper testing by medical professionals is necessary to determine the presence of allergies, and then to develop effective strategies for managing the allergic reaction. Understanding the process and purpose of food allergy testing for infants can help parents know what to expect and how to ensure their baby gets the best possible care.
Process of Food Allergy Testing
The process of food allergy testing for infants typically begins with a meeting between the doctor and the parents, during which the doctor tests the infant for signs of an allergic reaction. This can include skin prick tests, patch testing, and/or blood tests, depending on the suspected allergen.
The doctor may also recommend eliminating certain foods from the infant’s diet for a period of time in order to observe the results. After the testing has been done, the doctor can provide the parents with results and discuss strategies for managing any food allergies that are present.
Purpose of Food Allergy Testing
The purpose of food allergy testing is to identify any potential food allergies in infants, as well as to provide guidance on how to prevent and manage allergic reactions. Identifying a food allergy can also help parents to make choices about the types of food their baby eats and the environment in which they are exposed to foods. In addition, food allergy testing can help doctors identify any underlying medical conditions that may be contributing to the infant’s food allergies, such as asthma or eczema.
Managing Allergies: Implementing a Management Plan for Food Allergies in Babies
Implementing an effective management plan for food allergies in babies requires comprehensive knowledge of identifying, treating, and preventing allergic reactions. Parents are encouraged to talk to their doctor to learn more about their baby’s specific needs and develop an individualized plan. Generally speaking, food allergies in babies can be managed through a four-pronged approach.
- Identifying Allergens: The first step in managing food allergies in babies is to identify the allergens that are triggering the reaction. This can be done through an allergist-administered skin test or a blood test, which will indicate what, if any, foods are causing a reaction. Once the allergens have been identified, it is important to eliminate these foods from the baby’s diet.
- Avoiding Allergen Exposure: The second step in managing food allergies in babies is to avoid exposure to the allergen. This may mean eliminating any food containing the allergen, as well as avoiding contact with the allergen in any form, including airborne particles or trace amounts of the allergen. If a family member has a food allergy, it is also important to ensure that all surfaces and utensils are thoroughly washed after they have come into contact with the allergen.
- Treating Reactions: The third step in managing food allergies in babies is to be prepared in case of an allergic reaction. It is important for parents to be prepared to treat any reactions that may occur. This can include carrying an epinephrine pen and antihistamines, as well as knowing how to administer them properly and how to recognize the signs and symptoms of an allergic reaction. It is also important to know how to contact your doctor or local hospital in case of an emergency.
- Prevention: The fourth step in managing food allergies in babies is prevention. This can include introducing new foods to the baby slowly and testing for any reactions, as well as avoiding any foods that may increase the risk of an allergic reaction. This can also include cleaning surfaces and utensils thoroughly to avoid cross-contamination, and keeping an organized allergy-free environment in the home. Another important step in preventing an allergic reaction is reading labels carefully and avoiding any foods that may contain the allergen.
Support and Resources: Finding the Right Support and Resources to Help Parents Navigate Food Allergies in Babies
Food allergies in babies can be very daunting for parents, as they can cause an array of reactions that range from minor stomach aches to anaphylaxis. Because of how serious food allergies can be, it is crucial for parents to be aware of the risks and to be informed about the resources available to help them navigate a food allergy diagnosis.
In order to properly care for a child with food allergies, parents need to learn about the condition and how to identify, avoid and manage reactions. The following are some resources and support options that can help parents find the right support and resources to help their child.
Support Groups
Support groups can provide parents with much needed emotional support, as well as a space to share information and ask questions about food allergies. These groups can also help parents to connect with other parents who have experienced similar reactions and may have advice and recommendations on how to best manage the condition. Support groups can be found both online and in person and are usually run by organizations such as the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology and the Food Allergy & Anaphylaxis Network.
Medical Professionals
An allergist or pediatrician should be the first stop for parents looking for support and resources. An allergist can help to diagnose the condition and provide information about the specific allergies and how to manage them in a child’s daily life. They can also provide referrals to other medical specialists, such as a dietitian, who can help with designing an appropriate diet for the child. A pediatrician can also provide valuable advice and resources for parents navigating food allergies in babies.
Online Resources
The internet can be a great resource for parents looking for information about food allergies in babies. There are a number of websites and online forums devoted to discussing food allergies, providing resources and tips, and offering support. It is important to remember, however, that not all information found on the internet is reliable, so it is important to look for reputable sources.
Support Organizations
Support organizations such as the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology and the Food Allergy & Anaphylaxis Network offer a wealth of resources for those living with food allergies. They can provide information on how to recognize and manage reactions, as well as advice on how to create an allergen-friendly environment. These organizations also provide support services such as helplines and online forums, where parents can ask questions and get ideas from other parents.
Conclusion
Identifying and managing food allergies in infants can be a daunting task for parents. But with the right resources and knowledge, they can help ensure that their children stay safe and healthy. Parents should pay attention to signs and symptoms of food allergies and be proactive in identifying potential allergens.
Additionally, providing their baby with the proper nutrition and vitamins can help ensure that their infant’s immune system is working properly. Finally, parents should closely monitor their baby for any signs of food allergies and take appropriate steps to address any issues that arise. By taking these steps, parents can help ensure that their baby is safe and healthy.